α-Arbutin
α-Arubutin
α-Arbutin(Alpha Arbutin) is a new type of hydroquinone glucoside with an α-glucosyl bond. The manufacturing process was established by Ezaki Glico Co., Ltd., using the original transglycosylation enzyme developed by Ezaki Glico. Ezaki Glico succeeded, for the first time in the world, in industrial production of α-Arbutin by using their original enzyme and process.
Introduction
Ezaki Glico discovered that α-Arbutin has strong inhibiting effect on human tyrosinase. Indeed, the enzyme is involved in synthesis of melanin which causes freckles and suntan. These results studied by Ezaki Glico have been published in various scientific journals and presented at numerous conferences (please see the list of references).
Starting from 2002, α-Arbutin has been commercially sold to customers worldwide including Japan as a skin-lightening ingredient of cosmetics. α-Arbutin is sold through DSM Nutritional Products and is sold only in Japan through DSM Nutrition Japan K.K.
Various tests with respect to physicochemical features, stability and safety, as well as efficacy verification tests at the enzyme, cell and clinical levels have been conducted and those test results have been accumulated as our own data.
α-Arbutin manufactured by Glico Nutrition is a cosmetic ingredient that customers can use safely and comfortably.
Structure and Manufacturing Process
α-Arbutin is a new type of hydroquinone glucoside with an α-glucosyl bond. The research team of Ezaki Glico Co., Ltd has established the manufacturing process of α-Arbutin using their original transglycosylation enzyme that catalyzes alpha-anomer selective transglycosylation reaction.
< Chemical Structure and Name >
< Manufacturing Process >
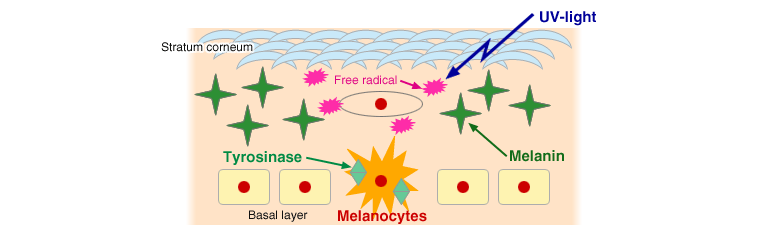
Mechanism of Melanogenesis Inhibition
The enzyme tyrosinase, one of the key enzymes involved in melanin synthesis, is activated in melanocyte by the stimulation of free radicals induced from UV irradiation and stress. Its activation triggers melanogenesis, a complex series of enzymatic and chemical reactions, and finally leads to the formation of freckles and suntan. The inhibitory effect of α-Arbutin on melanogenesis is thought to be due to direct inhibition of melanosomal tyrosinase activity.
< Mechanism of Melanogenesis >
< Mechanism of Melanogenesis Inhibition of α-Arbutin >
Efficacy
1.Inhibitory Effect on Tyrosinase
α-Arbutin suppresses melanin production that causes freckles and suntan.
Inhibitory effects of α-Arbutin on mushroom and human tyrosinases
Arbutin, β-anomer isoform of α-Arbutin, inhibited both mushroom and human tyrosinases. On the other hand, α-Arbutin selectively inhibited only human tyrosinase.
Inhibitory effect of α-Arbutin on human tyrosinase is estimated to be more than ten times stronger than that of arbutin.
| Mushroom a) | Human b) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | IC50 *1 | IC50 *1 | Ki *2 |
| α-Arbutin | Not detected | 1.8 - 2.1 mM | 0.2 mM |
| Arbutin (β) | 8 mM | > 30 mM | 4.2 mM |
- *1 : 50 % inhibitory concentration against tyrosinase activity.
- *2 : Parameter that shows the affinity of inhibitors for tyrosinase.
[References]
- a) M. Funayama et al., Effects of α- and β-Arbutin on Activity of Tyrosinases from Mushroom and Mouse Melanoma. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 59: 143-144 (1995)
- b) K. Sugimoto et al., Syntheses of Arbutin-α-glycosides and a Comparison of Their Inhibitory Effects with Those of α-Arbutin and Arbutin on Human Tyrosinase. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 51: 798-801 (2003)
2.Inhibitory Effects on Melanin Synthesis in Cultured Human Cells
α-Arbutin suppresses melanin production that causes freckles and suntan.
Effects of a-Arbutin on melanin production in a three-dimensional human skin model
Darkening of the melanocytes in a three-dimensional human skin model was clearly inhibited by treatment with α-Arbutin.
Melanin production in melanocytes was restored by withdrawal of treatment of α-Arbutin, and no significant difference in cell viability between α-Arbutin-treated and non-treated tissues was observed. These results suggest that the topical treatment of α-Arbutin decreased melanin synthesis in the human skin model without affecting cell viability.
< Microscopic views of Cultured Human Skin Model with and without α-Arbutin (X100) >
[References]
- K. Sugimoto et al., Inhibitory Effects of α-Arbutin on Melanin Synthesis in Cultured Human Melanoma Cells and a Three-Dimensional Human Skin Model. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 27: 510-514 (2004)
Effects of a-Arbutin on melanin production in cultured human melanoma cells
α-Arbutin showed dose-dependent inhibition of melanin production in cultured human melanoma cells without affecting cell viability.
3.Clinical Study
Clinical Study of Efficacy for Skin-Lightening
We evaluated skin-lightening effects by clinical study involving 60-human volunteers. The cream containing 1.0 % α-Arbutin lightened the color of the skin and it shows better skin-lightening efficacy than the competitive ingredients, such as Arbutin, Kojic acid and Hydroquinone within a short time, 1 month. Effects of α-Arbutin were sustained during the study period, three months.
(Methods)
- Study subject : 20 persons / group
- Treatment : treated twice daily with test cream containing 1 % active ingredient
- Evaluation : objectively by colorimetry at M0 and M1
Clinical Study of Efficacy for Prevention of Pigmentation Induced by Ultraviolet Irradiation
We examined the inhibitory effect of α-Arbutin toward pigmentation induced by ultraviolet irradiation. As compared with a control cream preparation, a cream preparation containing 2.0 % α-Arbutin had a significant degree of ability to suppress pigmentation induced by ultraviolet irradiation, in the same manner as a cream preparation containing 3.0 % sodium ascorbyl phosphate. It was also confirmed that a cream preparation containing 1.0 % α-Arbutin had a tendency to suppress melanogenesis induced by ultraviolet irradiation, although this effect was weak as compared with that of the cream preparation containing 2.0 % α-Arbutin and the cream preparation containing 3.0 % sodium ascorbyl phosphate.
(Methods)
- Study subject : 23 persons
- Treatment : treated twice daily with test cream preparations
- UV-irradiation : one time (the first day of the test)
- Evaluation : objectively by colorimetry before (week 0) and at weeks 1, 2, and 3.
Specifications
Specifications
For further information please contact us.
Name
| Trade name | α-Arbutin |
| INCI name | Alpha-Arbutin |
| Chinese INCI name | α-熊果苷 |
Other Information
| CAS No. | 84380-01-08 |
| ELINCS No. | 440-470-8 |
References
[ Research Papers ]
- "Purification and Some Properties of α-Amylase from Bacillus subtilis X-23 That Glucosylates Phenolic Compounds Such as Hydroquinone"
T. Nishimura et al., J. Ferment. Bioeng. 78, 31-36 (1994) - "Inhibitory Effects of Hydroquinone-α-glucoside on Melanin Synthesis" (in Japanese)
T. Nishimura et al., Yakugaku Zasshi 115, 626-632 (1995) - "Enzymatic Production and Utilization of α-Arbutin" (in Japanese)
T. Nishimura, Bioscience and Industry 61, 259-260 (2003) - "α-Arbutin: a new skin-lightening agent for cosmetics" (in Japanese)
K. Sugimoto, J. Appl. Glycosci. 50, 109-110 (2003) - "Syntheses of Arbutin-α-glycosides and a Comparison of Their Inhibitory Effects with Those of α-Arbutin and Arbutin on Human Tyrosinase"
K. Sugimoto et al., Chem. Pharm. Bull. 51, 798-801 (2003) - "The More Effective, Faster and Safer Approach to Skin Lightening and Liver Spot Minimizing"
H. Ziegler et al., PERSONAL CARE January, 15-18 (2003) - "Inhibitory Effects of α-Arbutin on Melanin Synthesis in Cultured Human Melanoma Cells and a Three-Dimensional Human Skin Model"
K. Sugimoto et al., Biol. Pharm. Bull. 27, 510-514 (2004) - "Syntheses of α-Arbutin-α-Glycosides and Their Inhibitory Effects on Human Tyrosinase"
K. Sugimoto et al., J. Biosci. Bioeng. 99, 272-276 (2005) - "Inhibitory Effects of Several Types of Hydroquinone Glycosides on Human Tyrosinase and Melanogenesis Inhibition of Alpha-Arbutin"
K. Sugimoto et al., FRAGRANCE JOURNAL 33, (5) 60-66 (2005) - "Experimental study on cross-reactivity of α-Arbutin toward p-phenylenediamine and hydroquinone in guinea pigs"
K. To-o et al., J. Dermatol. 37, 455-462 (2010)
[ Research Presentations ]
- "Inhibitory Effects of α-Arbutin on Melanin Synthesis -1-"
K. Nomura et al., The Society for Biotechnology, Annual Meeting 2002 - "Inhibitory Effects of α-Arbutin on Melanin Synthesis -2-"
K. Sugimoto et al., The Society for Biotechnology, Annual Meeting 2002 - "Inhibitory Effects of Several Types of Hydroquinone Glycosides on Human Tyrosinase and Melanogenesis Inhibition of Alpha-Arbutin"
T. Nishimura et al., IFSCC 2003 - "Melanogenesis Inhibition of α-Arbutin and Inhibitory Effects of Various Types of Hydroquinone Glycosides on Human Tyrosinase"
K. Sugimoto et al., The Ninth Japan-China-Korea Joint Symposium on Enzyme Engineering (2006)
Contact Us
| for enquiries, contact | Global Sales Department, Technical Sales Division, Glico Nutrition Co., Ltd. 4-6-5, Utajima, Nishiyodogawa-ku, Osaka 555-8502 Japan E-MAIL: g-ingredients@glico.com * When you contact us, please let us know your name, company and country in the message. |
| Sole reseller : | DSM Nutritional Products Ltd. Personal Care Building 241/1019 P.O. Box 2676 CH-4002 Basel, Switzerland Phone: +41 61-815-88-13 FAX: +41 61-815-85-90 DSM Nutrition Japan K.K. 2-6-3, Shiba Koen, Minato-ku, Tokyo 105-0011 Japan Phone: +81 3-5425-3758 FAX: +81 3-5425-3775 |